1. Materials: Sputum smear microscopy slides from 12 patients prepared using the Kinyoun acid-fast stain and counterstained with methylene blue solution
2. Images acquisition:
2.1 Equipments: a Canon PowerShot A640 -10 megapixels digital camera, attached to a conventional microscope model Zeiss Axioskop 4.
2.2 Number of images: 120 images
2.3 Spatial Resolution: 2816 x 2112 pixels.
3. Grouping of images:
The images acquired were classified in four groups based on: 1 – background density; 2 – density of bacilli (see figure 2). The “High Density Background” group is characterized by a strong presence of counterstain with methylene blue solution in the background, while the “Low Density Background” group is characterized by a weak presence of this counterstain.
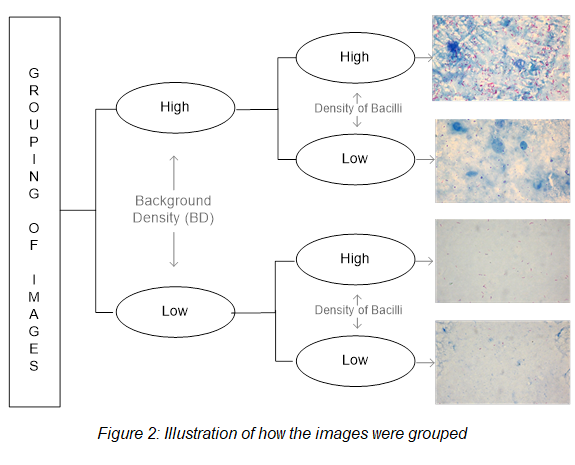
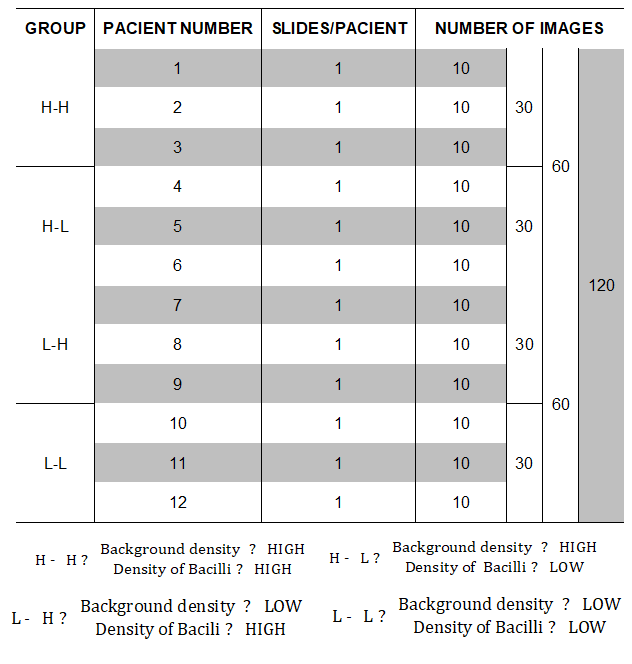
Table 1 shows the distribution of images into groups.
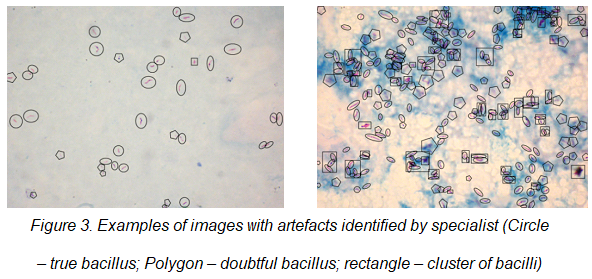
4. Image analysis by a specialist
All acquired images were submitted to a specialist in order to identify the bacilli, clusters of bacilli and other artifacts named as doubtful bacilli. Each kind of identified object was surrounded by a specific geometric shape (see figure 3):
· A true bacillus was surrounded by a circle.
· A cluster of bacilli was surrounded by a rectangle, and
· A doubtful bacillus surrounded by a polygon.
The images with marked objects could be used as gold standard to evaluate the accuracy; sensitivity and specificity of bacilli recognition.